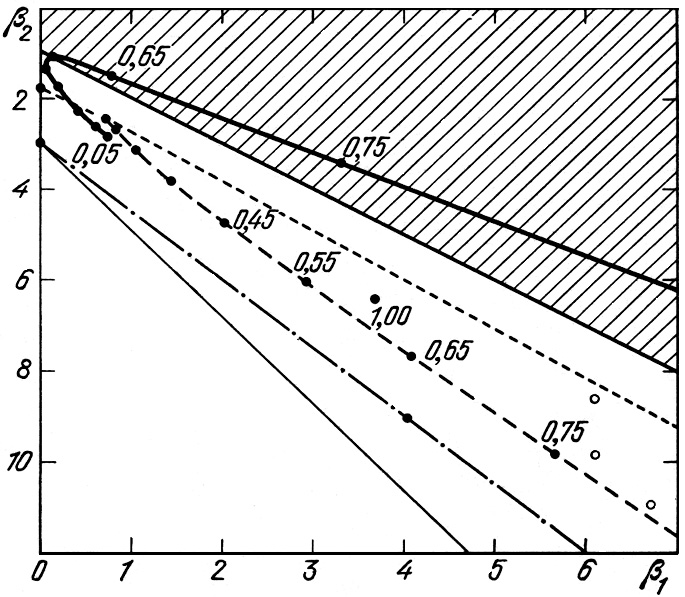
The Pearson diagram
跳到导航
跳到搜索
The Pearson diagram, Two of its coordinates are the dimensionless indices of skewness (B1,三阶矩) and kurtosis(B2,四阶矩) which uniquely characterize the form of the distribution. 参见 [1]
- For example, uniform and normal distributions appear on the (B1,B2)diagram as the points (0, 1.8) and (0, 3).
- An exponential distribution on this diagram appears at point (4, 9).
- A gamma distribution has the form of a straight line, shown as the dot-dash line, extending beyond the two last points.
- A log-normal distribution is the light solid line below this.
- The shaded part of the Pearson diagram indicates a critical zone (B1< 0 and B2<B1+ 1), where no actual distribution of the desired form can exist.Between this critical line B2= B1+ 1 and the line corresponding to gamma functions is the region of beta distributions.This consists of zones for the U-like or bi-modal, and J-like or uni-modal, distributions.